| 10 Status of Residence and Alien Registration |
1. Status of Residence
2. Changing Status of Residence
3. A permit for extra-status activities (e.g. a person intends to engage in
a part-time job)
4. Extension of period and stay
5. Illegal Employment and Deportation
6. Alien Registration
1. Status of Residence
Foreign nationals residing in Japan are authorized to engage in the activities
(Business and Employment, and so on) which fall under their status of residence
granted at the time of their entry into Japan, and they are permitted to
stay in Japan within the period of stay determined according to their status
of residence.
When a foreign national wishes to change his/her status of residence after entry; extend his/her period of stay or obtain a permit for extra - status activities, it is necessary to apply at the Immigration Bureau.
A foreign national residing in Japan must
carry his/her passport with him/her at all times. However, if he/she has
received ag Certificate of Alien Registrationh and carries it with him/her,
he/she need not carry his/her passport. In case a foreign national has
lost his/her passport, it is necessary that a new passport or a substitute
is issued by the embassy of his/ her home country in Japan.
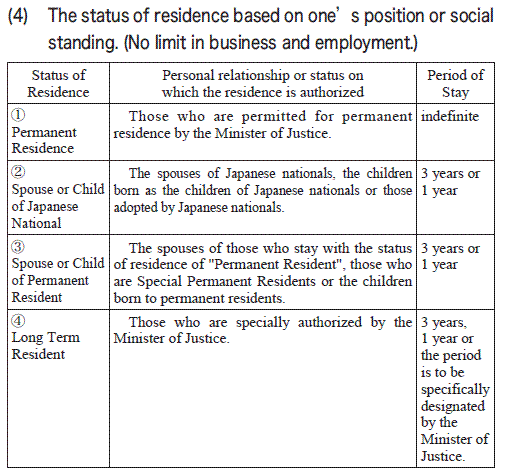
The list of status of residence under the
Immigration Control Act is shown in the following table
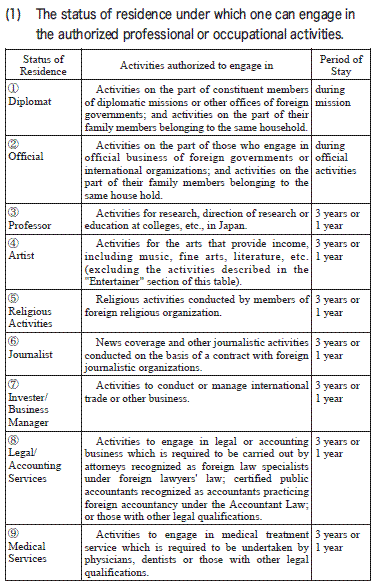
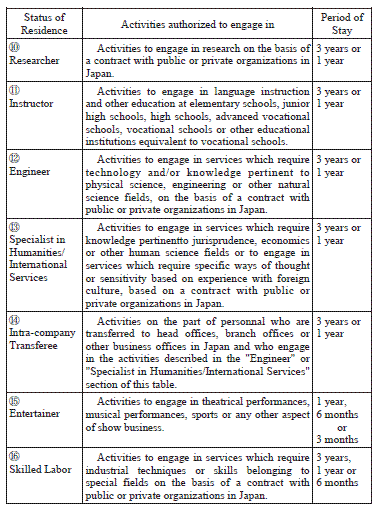
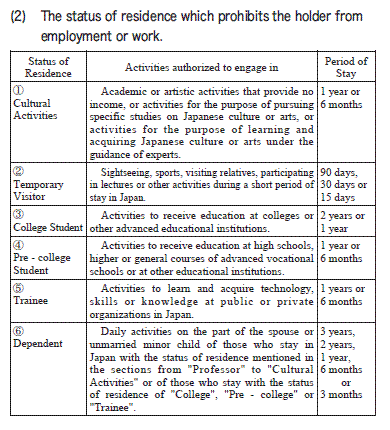

Period of Stay
1, 3Years, 1 year of 6 months
2, the period which the Minister of Justice designates for each foreigner within a one year period
2. Changing Status of Residence
It is necessary to apply to change one's status of residence if a foreign national desires to change it.
(1) In the case of a change in occupation;
Permission is needed from the Immigration
Bureau when a change of occupation will affect the status of residence.
For instance, a person, whose status isg Specialist in Humanities /International
Servicesh, gives up his/her job and begins to teach at a college with the
status ofg Instructorh, requires permission to change status.
It is not necessary to file previously with
the Immigration Bureau an application for change of status when a person
takes up other employment, if the activity comes under the same status
as already held. However, if the person concerned feels some anxiety on
his/her change in occupation, he/she may file an application for the certificate
of authorized employment, for the purpose of confirmation by submitting
the documents showing the details of a new working place. If he/she does
not have the certificate of authorized employment, it is necessary to submit
relevant documents showing the details of any change in employment when
next applying for extension of period of stay. An example would be that
a cook, whose status is gSkilled Laborh, changes only his/her working place,
and is still employed as a cook.
It is essential that a report is made to
the mayor or head of the ward, city, town or village within 14 days, when
foreign nationals change thier jobs. (Article 9- 1, Alien Registration
Act)
(2) In cases of employment when under a status prohibiting work
An application for changing status of residence
is required when a student under ag college studenth status hopes to be
employed in Japan after his/her graduation. (Article 20, Immigration Control
Act)
In principle, the status of a gtemporary
visitorh cannot become employed. He/she should leave Japan in order to
get a new visa at a Japanese embassy or legation abroad. Then the foreign
national will be able to re - enter with a suitable visa for his/her proposed
activity.
However it is possible to change the status of residence, based on social status or relationship. An example is that when a foreigner, whose status does not allow employment, changes his/her status tog Spouse or child of Japanese Nationalh as a result of getting married to a Japanese national, it is not necessary to leave Japan for a new visa.
3. A permit for extra-status activities (e.g. a person intends to engage
in a part-time job)
A person needs to apply for and obtain permission in advance at the Immigration Bureau, in order to be able to engage in an activity other than that permitted by the status of residence previously granted.
Such a person would be a college student
or a pre ? college student who wants to have a part - time job. An application
for those students is made by the educational organization, and permission
is generally given without restrictions on working time zones or place,
except for business which may affect public@ morals. Working hours shall
be limited to up to 28 hours a week@(14 hours for a auditor).
It is also necessary to get a permit when
a foreigner, whose status does not allow work, for exampleg Cultural Activitiesh,
wishes to work as a part - timer. He/she should report the occupation's
duties and place to the Immigration Bureau before starting a part - time
jobs
4. Extension of period and stay
The period of stay is determined together with the status of residence at the time of landing, the change of status of residence, etc. A foreign national is permitted to stay in Japan within the period of stay thus determined. Therefore, a foreign national who wishes to extend his/her period of stay should apply for permission for an extension of period of stay, not later than the expiry date of the authorized period of stay. An application for extension of period of stay will be accepted from about one month prior to that date.
Anyone who stays in Japan beyond his/her
authorized period of stay may be subjected to punishment and/or deportation
(Article 24 Item 4 and Article 70 Item 5, the Immigrat
5. Illegal Employment and Deportation
(1) Illegal Employment
The following are examples of cases of "Illegal Employment";
a.@Employment activities of foreigners without the proper status of residence, who enter illegally or stay beyond the authorized period of stay.
b.@Employment activities above and beyond the status of residence undertaken without permission.
Illegal workers may be subject to punishment
and/or deportation.
And the persons, who employ these illegal workers might also be subjected to punishment for the crime ofg assisting of illegal workersh. (The punishment is imprisonment for up to 3 years and/or a fine of up to 3,000,000.)
(2) Deportation
Foreigners may be deported from Japan under the
Immigration Control Acts for the following reasons;
a.@illegal entry,
b.@illegal landing,
c.@illegal over staying,
d.@illegal activities other than those permitted by their status of residence and
e.@violation of Acts and regulations.
The procedure of deportation is as shown below, to take into account the foreigner's human rights.

If your passport is lost or not in your possession
it is essential that you be issued a replacement passport or a substitute
at the Embassy of your home country in Japan.
6. Alien Registration
All foreign nationals residing in Japan are required to register within 90 days of their arrival in Japan, at the municipal office of the city, ward, town, or village in which they are living. When the registration has been carried out, a certificate of Alien registration bearing the registered information will be issued to the registrant by the mayor or headperson of the ward, city, town or village.
When any change occurs in the registered
information, which may be about the place of residence, etc., @it is necessary
to inform the mayor or headperson. All registrants (except persons under
the age of 16 years) are required to apply for confirmation of registered
information (an gApplication for Confirmation of Registered Informationh)
every 5 years.@
An application for re-issue of a lost certificate
is required@within 14 days of the loss.
|